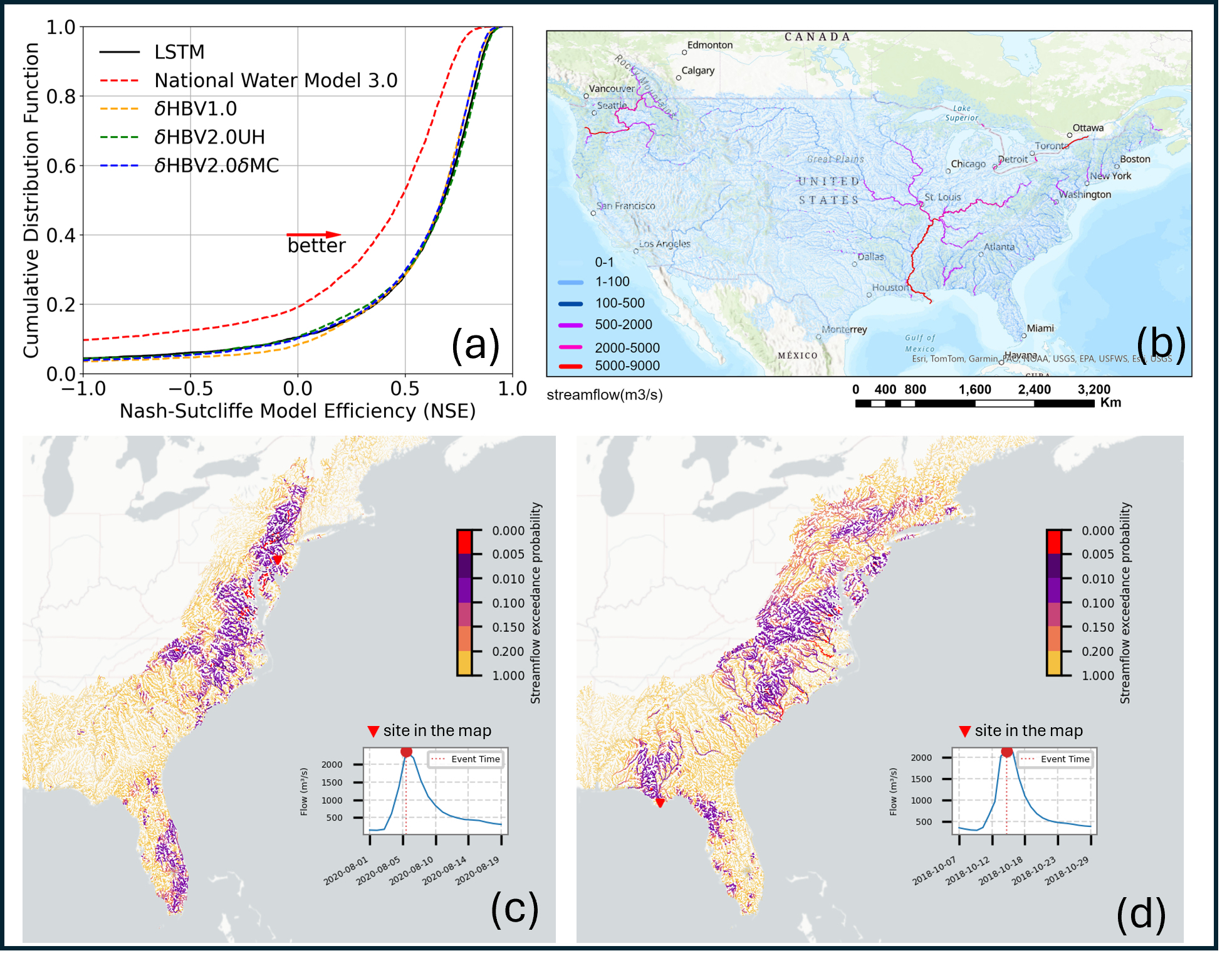
Assessing Streamflow Forecast Over the Hackensack River Watershed Using NGIAB

A poster presented by the I-SMART team at the CIROH Developers Conference, held at the University of Vermont in Burlington from May 28 to 30, 2025.
The densely populated Hackensack River watershed lies within the New York City Metropolitan Area, which spans northern New Jersey and southern New York. Accurate streamflow forecasting within this region is therefore essential to enable effective water resource management, flood prediction, and disaster preparedness.
Precipitation data is critical for effective hydrological modeling, making the identification of reliable data sources a key priority. This is why the Integrated Spatial Modeling and Remote Sensing Technologies Laboratory (I-SMART), an interdisciplinary research unit within the Davidson Laboratory at Stevens Institute of Technology in Hoboken, New Jersey, uses the latest developments in both atmospheric and hydrological modeling to address flood risks in the Hackensack Watershed with solutions that could be expanded to the entire New York City Metropolitan Area.