AORC Data in Your Hands: User-Friendly Jupyter Notebooks for Data Retrieval and Analysis via CIROH JupyterHub Notebooks
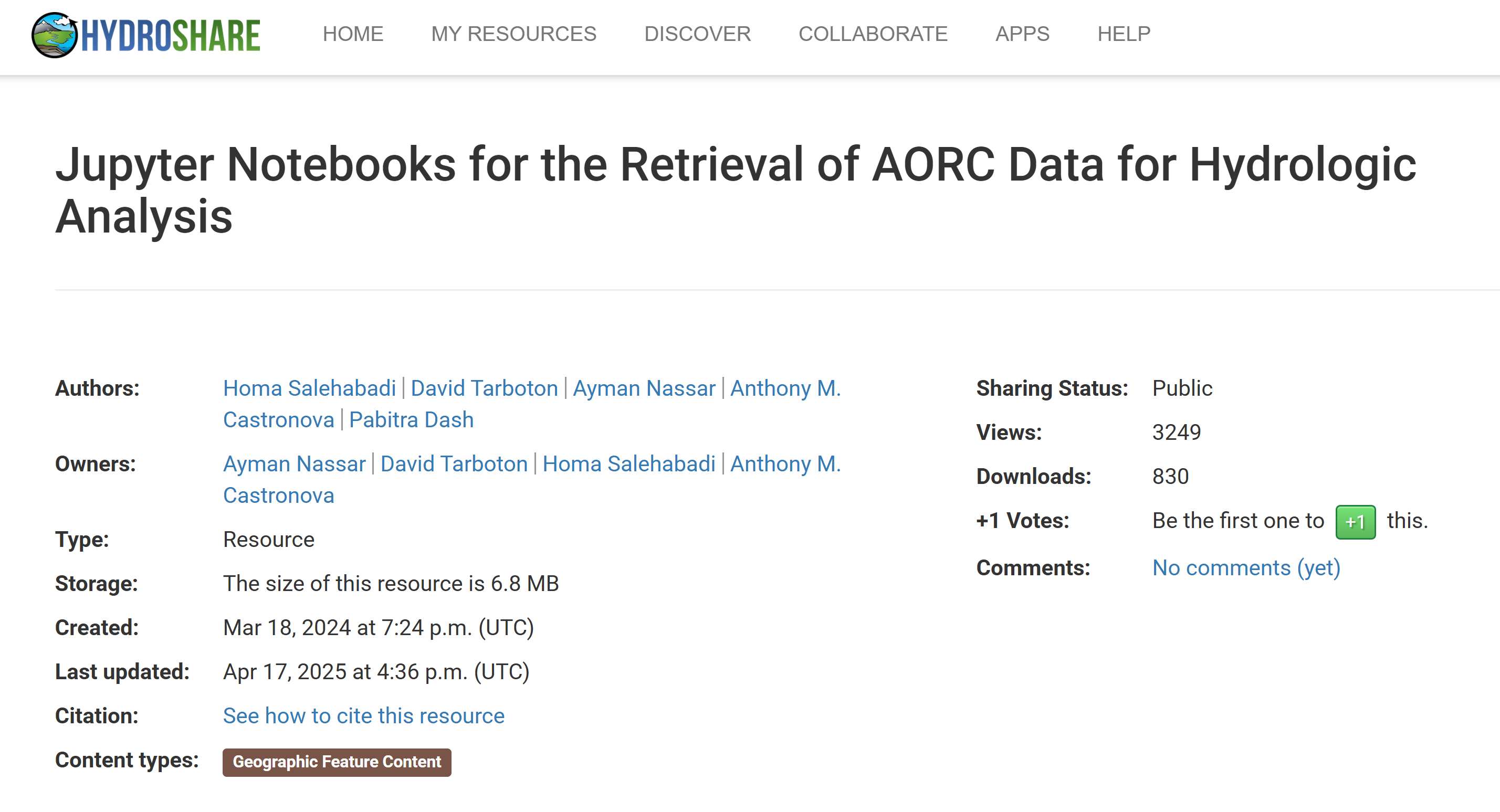
The Analysis of Record for Calibration (AORC) dataset is recognized as a high-value resource for the CUAHSI and CIROH community. This dataset is hosted by NOAA via Amazon Web Services (AWS) and is available in two primary formats: a latitude-longitude gridded dataset and the National Water Model (NWM) projected dataset, part of the NWM Retrospective archive. To enhance accessibility and illustrate analysis capabilities, we developed four user-friendly Jupyter Notebooks that enable data retrieval for both specific points of interest and spatial domains defined by shapefiles:
- AORC_LL_PointRetrieval.ipynb: For retrieving and aggregating data from the latitude-longitude gridded dataset for a specific point using geographic coordinates.
- AORC_LL_ZoneRetrieval.ipynb: For retrieving and aggregating data from the latitude-longitude gridded dataset for an area defined by a polygon shapefile.
- AORC_NWMProj_PointRetrieval.ipynb: For retrieving and aggregating data from the NWM projected dataset for a specific point using geographic coordinates.
- AORC_NWMProj_ZoneRetrieval.ipynb: For retrieving and aggregating data from the NWM projected dataset for an area defined by a polygon shapefile.
These Jupyter Notebooks, containing instructions and Python code to access the data, enable researchers to retrieve AORC data from AWS. From there, the notebooks offer options to subset and aggregate the data over user-defined time intervals (beyond the original hourly resolution) and spatial area. These serve as examples for how you could write or modify code to access AORC data in your work. The notebooks are publicly available on HydroShare and are compatible with JupyterHub computing platforms such as CIROH 2i2c JupyterHub linked to HydroShare.
To use these notebooks, go to the HydroShare resource, select "Open With" at the top right, and choose "CIROH 2i2c JupyterHub". This will copy the resource contents (notebooks and data) into the CIROH JupyterHub environment, where you can open and work through them to access the data. Note that you will need a CUAHSI HydroShare account to access "Open With" in HydroShare, and you will also need to request CIROH-2i2c JupyterHub access using a GitHub account.
Our work also includes a comparative analysis of the two AORC datasets with a summary of findings. While we mostly observed small differences, mainly due to projections, users should be aware of potential discrepancies between the datasets.
By providing these user-friendly tools and highlighting the characteristics of both AORC datasets, our work aims to support and facilitate more efficient hydrological and climate-related research within the CUAHSI and CIROH community.
References:
- Salehabadi, H., D. Tarboton, A. Nassar, A. M. Castronova, P. Dash (2025). Jupyter Notebooks for the Retrieval of AORC Data for Hydrologic Analysis, HydroShare, http://www.hydroshare.org/resource/72ea9726187e43d7b50a624f2acf591f
- The development versions of these notebooks are available on GitHub: https://github.com/CUAHSI/notebooks in the Data Access Examples / AORC - Retrieval of AORC Data for Hydrologic Analysis folder.
- Patel, A., A. Castronova (2025). CIROH 2i2c JupyterHub, HydroShare, http://www.hydroshare.org/resource/2dd1ac86e8854d4fb9fe5fbafaec2b98

















 Image Source:
Image Source: