CIROH Cloud User Success Story
· 3 min read
This month, we are excited to showcase two case studies that utilized our cyberinfrastructure tools and services. These case studies demonstrate how CIROH's cyberinfrastructure is being utilized to support hydrological research and operational advancements.
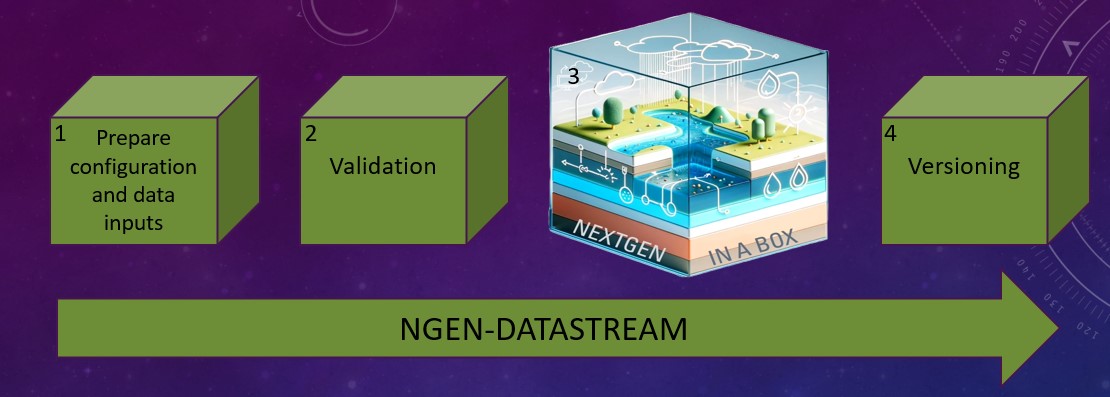
1. ngen-datastream and NGIAB